When deciding on which blockchain to issue a security token, an important factor is the software protocol used to represent the asset on the blockchain. Each software protocol has different options for the issuer, and certain exchanges only work with certain protocol standards.
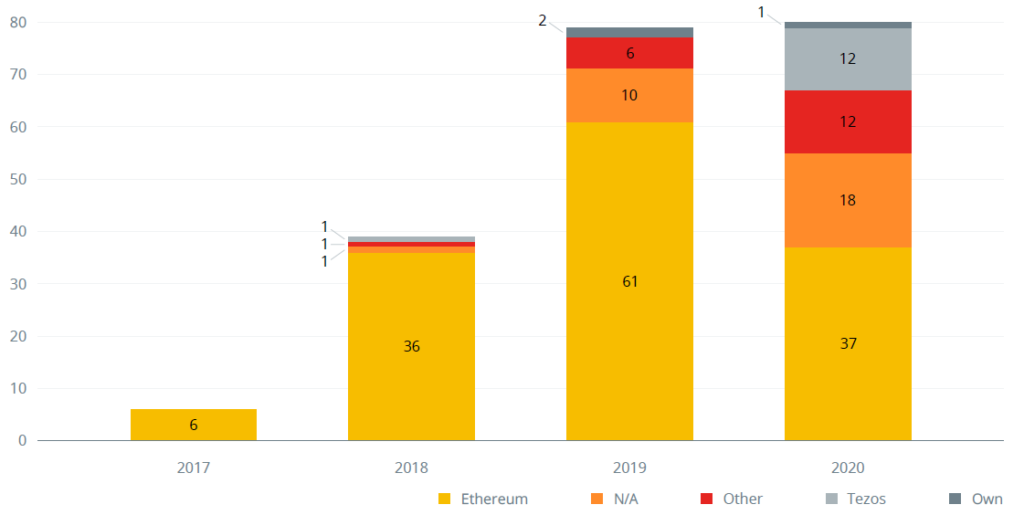
Ethereum remains by far the most popular platform for security token offerings, because it has huge liquidity, simply created smart contracts and well-known standards for token issuing. Moreover, there are lots of wallets, exchanges and platforms that are ERC compatible, where holders and issuers can easily store, transfer, and manage their tokens.1
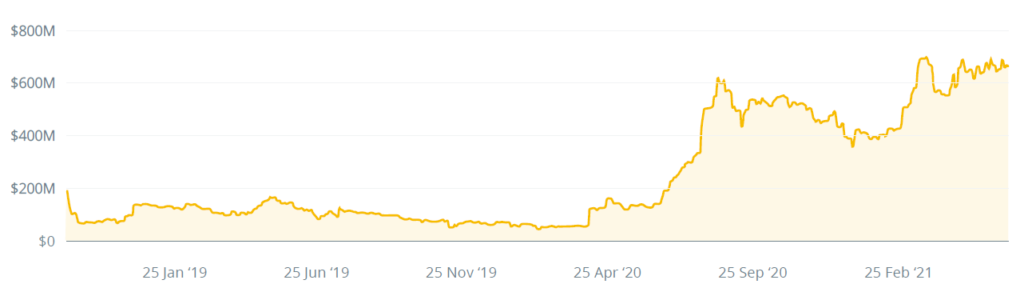
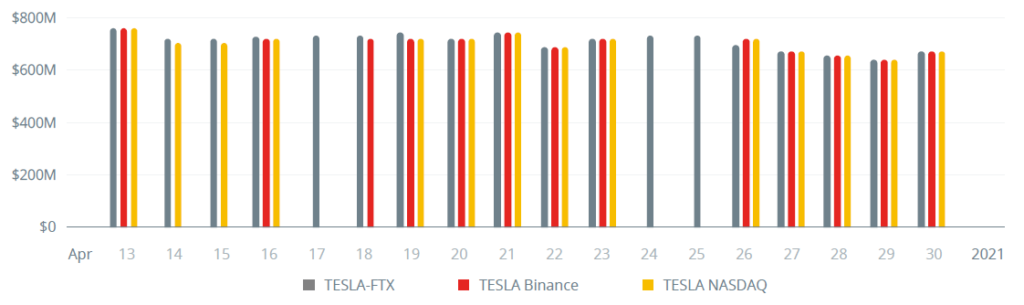
Overstock, which is the largest security token project on the market, is made with the ERC-20 standard. Overstock is a large NASDAQ listed internet retailer which specializes in furniture sales. OSTKO token allows its holders to get dividends. Its market cap is more than $280 million and daily trading volume is around $100,000.2
Ethereum’s dominance is not as large as it was in previous years, and it seems that projects are looking for alternatives. Tezos is the second most popular blockchain for security token issuance and trading. There are now more than $2.5 billion STs announced with the usage of Tezos blockchain. Tezos smart-contracts are more flexible for security token offering needs, having compliance and regulation features built-in. Elevated Returns was a pioneer in the security token industry and issued one of the the first security token backed by a trophy real estate asset, the St Regis Resort in Aspen, in 2018.
The Aspen Coin, which was initially issued as an ERC20 token, is now hosted on the Tezos blockchain, deemed by Elevated Returns as the best blockchain for STO’s. The Aspen Coin is more significant by its structure than by its size. Since inception, a total of 12% have been paid out to token holders as distributions, both in fiat and cryptocurrency. The token is now trading on the tZERO ATS. Furthermore, Aspen Coin offers additional features like perks attached to the ownership of the token. The perks are financial such as up to 50% cash back on a hotel stay as well as access to unique experiences only available to members.
Elevated Returns has recently created a completely regulated digital finance ecosystem, which is going live this summer (July 2021) in South East Asia. The Elevated Returns team has spent 2 years acquiring licenses and made a major investment in Xspring Capital which owns a regulated security token platform in Thailand. This will bring to the market the first unrestricted regulated public offering with simultaneous listings on a regulated exchange. The token is backed by a real estate asset and will be listed on the ERX digital asset exchange. There are several large companies aiming to launch their future STOs using Tezos blockchain — tZERO, BTG Pactual, Dalma Capital, Fundament group and some others.3
Number of STO by issuing platform, 2017 – 2020
Ethereum-based Security Tokens
Types of Ethereum-based Tokens
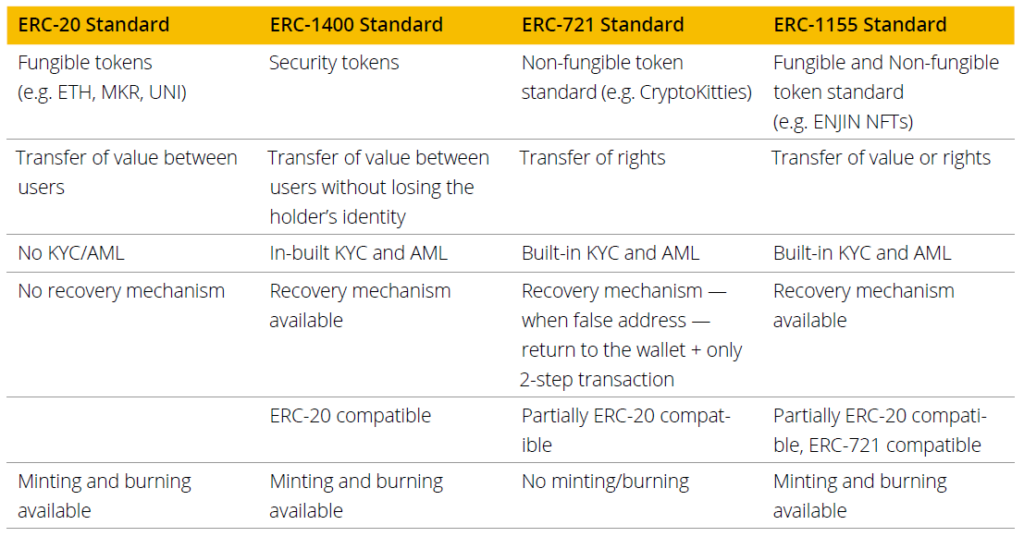
In order to be compatible with wallets and blockchains, an issuer must use the same standards as the other players. However, the ERC-20 doesn’t allow for the enforcement of the rules and regulations that govern private securities. A few of the options that security token issuers are looking for when choosing an appropriate standard include:
1. Encoded Compliance — The transfer rules are embedded in the securities and can never be transferred to an ineligible individual in either the primary or secondary markets.
2. Reduced Costs — Fees to do with settlement and reconciliation are dramatically reduced with compliant P2P transfers.
3. Controlled Securities — Issuers remain in control of the tokens, even with investor self-custody.
4. Increased Transferability — the reduction of friction points across the value chain unlocks highly transferable assets.
The ERC-20 protocol is the original and oldest standard for issuing tokens. However, it has its own vulnerabilities and disadvantages. For example, tokens can be drained from the smart contract with no recovery possible, or an investor could not retrieve their tokens if they sent them to a non-ERC-20 wallet or smart contract or if the holder loses his private key. There are also compliance and regulatory issues such as being difficult to set all the necessary KYC and AML procedures inside the ERC-20 standard. For example, you cannot enforce KYC for secondary market trading. In that case, many alternative protocols were developed to help suit the security token market’s needs. All those alternatives (ERC-1400, ERC-721, ERC-1155, etc) are compliant with the ERC-20 standard which means that they can be easily stored, exchanged and transferred with ERC-20 infrastructure.4 5 6 7
Alternatives to Ethereum’s ERC-20 include:
DS Protocol
DS is an open-source protocol , which was designed by Securitize specifically for securities and supports third-party applications. It has special DS apps, which address relevant events connected to the tokenized economic rights (issuance, trading, cap-table generation, governance events, required pay-outs). This protocol also has integrated compliance and registry services. Tokens made with the use of this protocol are user-friendly — it is easy for holders to manage their tokens and they regularly receive various updates related to their tokens.
Current Media’s CRNC token. It is a token of a reward based streaming platform Current, which pays its users for using their service and providing data. The token is aimed at giving users better rewards while engaging the media.
Blockchain Capital token BCAP is also based on DS protocol. Blockchain Capital is a large venture capital firm specializing in investing in blockchain based projects. Blockchain Capital used DS protocol for their STO due to the compliance, regulations and security features offered by Securitize for their security token.
R-Token
R-token is an ERC-20 type token made by Harbor with some extra features added: in-built KYC, AML and taxation services as well as some flexible functionality which helps the issuer to make the necessary regulatory configuration. R-token standard allows the creation of tokenized regulated securities.
Harbor, which created R-token, was acquired by the most popular digital asset custodian BitGo in 2020 and gained broker-dealer and transfer agent licenses. BitGo, in turn, was recently acquired by Galaxy digital — one of the most significant digital asset focused VC. We see those acquisitions as a possibility for BitGo to become a clearing house for the security tokens.
iCap Equity which is a real estate firm based in Seattle is using Harbor R-token for tokenizing its assets.
T-REX
T-REX is a protocol built on the public Ethereum blockchain which was created by Tokeny Solutions, which has been recently been renamed Tokeny Sarl. Although T-REX is Based on the ERC-20 standard, it has more than 100 options that can be used by issuers in order to enforce compliance and manage control for the issuer, agents, and investors.
Tokeny Sarl state that they have more than $8.5 billion of tokenized assets with the help of their T-REX protocol.
For example, Metalstream — a South-East Asian precious metal company. Their tokens are backed by gold and as it is stated by the token issuers — 1000 MSGLD tokens can be exchanged for 1 kilo of gold. Also, the token holders can get a discount on purchasing gold of up to 40% of market spot price.
SFT
SFT protocol by Hyperlink Capital uses Solidity programming language which is used by ETH developers, that makes the SFT part of the ETH network. Basically, this protocol is similar to ERC-20 with the same comfy features which allow to easily build a smart contract. However, it is more complex and secure and that is why, allowing to tokenize debt and equity-based securities.
ERC-1404
ERC-1404 was developed by Tokensoft and based on the ERC-1400 standard and is the ETH based SEC approved standard for security tokens. Which means that it fulfils the necessary security and compliance requirements including in-built KYC and AML (both for primary and secondary market).
Tokensoft launched its own STO based on their ERC-1404 standard. Tokensoft is one of the most significant security token platforms on the market. It has a platform for launching STOs as well as asset management features. What is also interesting, Tokensoft is permitted to deal with SEC registered securities.
Nevertheless, Ethereum is not the only platform out there that allows its users to issue a Security Token. That is why we will dedicate another article to Tezos and other blockchain platforms next week.
1 https://www.leewayhertz.com/launch-sto-security-token-offering/
2 https://stomarket.com/sto/overstock-ostko
3 https://medium.com/tezoscommons/security-tokens-on-tezos-why-tezos-4a7065f49a06
4 https://micobo.medium.com/security-tokens-an-erc-standards-comparison-919e7c379f37
5 https://medium.com/ethex-market/the-ethereum-blockchain-and-erc20-tokens-technical-challenges-and-solutions-for-2019-and-beyond
6 https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/555-erc20-token-vulnerability
7 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OZVlMXwOlXM
This article is an extract from the 90+ page Security Token Report 2021 co-published by the Crypto Research Report and Cointelegraph Consulting, written by thirteen authors and supported by Crypto Finance, Blocklabs Capital Management, HyperTrader, Ten31 Bank, Stadler Völkel Attorneys at Law, Riddle&Code, Coinfinity, Bitpanda Pro, Tokeny Solutions, AlgoTrader, and Elevated Returns.